What are user roles and why would you use them on your WordPress site?
WordPress allows five different types of roles that can be assigned to anyone you would like to contribute to your site (= a user). If no one else adds content to your site, you probably don’t need the info we’re going to share in this post. It’s a different story when you involve others to write or share articles, photos or videos for you.
User roles
A user role is a set of tasks (e.g. create, edit) that can only be done by a user whom the role was assigned to. A user role can be assigned to one or more users. Each user role has certain access to the backend of your site, with different capabilities and restrictions. As the owner/administrator, you determine the set of restrictions a user should have as a member of your team or community.
A safe site
To keep your site safe, you should be careful when you allow others access to your dashboard. Here’s an example of why you also want to keep an eye on your users.
After several unsuccessful login attempts as the admin of a site we manage, we finally figured out that there was another user listed under the name Admin. Fortunately this user didn’t have Admin rights, but was a Subscriber with very limited access.
Whether it was a person or a robot, someone was trying to force their way in by signing up as a user to access our Dashboard! That’s why it is important to understand the different user roles and capabilities before you decide to give others access.
The five user roles in WordPress
Administrator (Admin) – The administrator has the highest level of access and can make any changes to a WordPress site from the backend or dashboard. This role is created when you first set up your site, but it can also be assigned to someone else by you, the Admin. You’ll have two Admins with the same authorities, so be sure you can fully trust this person to act on your behalf. Like we said, the Admin can do anything:
- Create, edit, and delete content
- Manage plugins and themes
- Edit code of plugins or themes
- Create or Delete other user accounts
Editor – An editor also has a high level of access, but this is limited to content only. The editor can manage content on both pages and posts, even those written by others. Capabilities of an editor are:
- Create, edit, delete and publish content
- Moderate comments
- Manage links and categories
Author – As an author, a user can manage their own content and nothing more. They can create, edit, delete and publish posts and media files, but not what others produced.
Contributor – A contributor can read all posts, but only edit and delete their own. This is a very limited role because this user is not enabled to publish post or upload media files.
Subscriber – The subscriber role is very limited and really only useful when you want to give a user access to i.e. a membership site. Subscribers can read all posts (like any visitor) and manage only their own profile.
Assigning user roles
Go to the WordPress Dashboard.
Go to Users, then click on Add New.
This screen is also used to change the role of an existing user.
Insert Username, Email, First Name, Last Name and Website.
Adjust (User) Role, then click on Add New User.
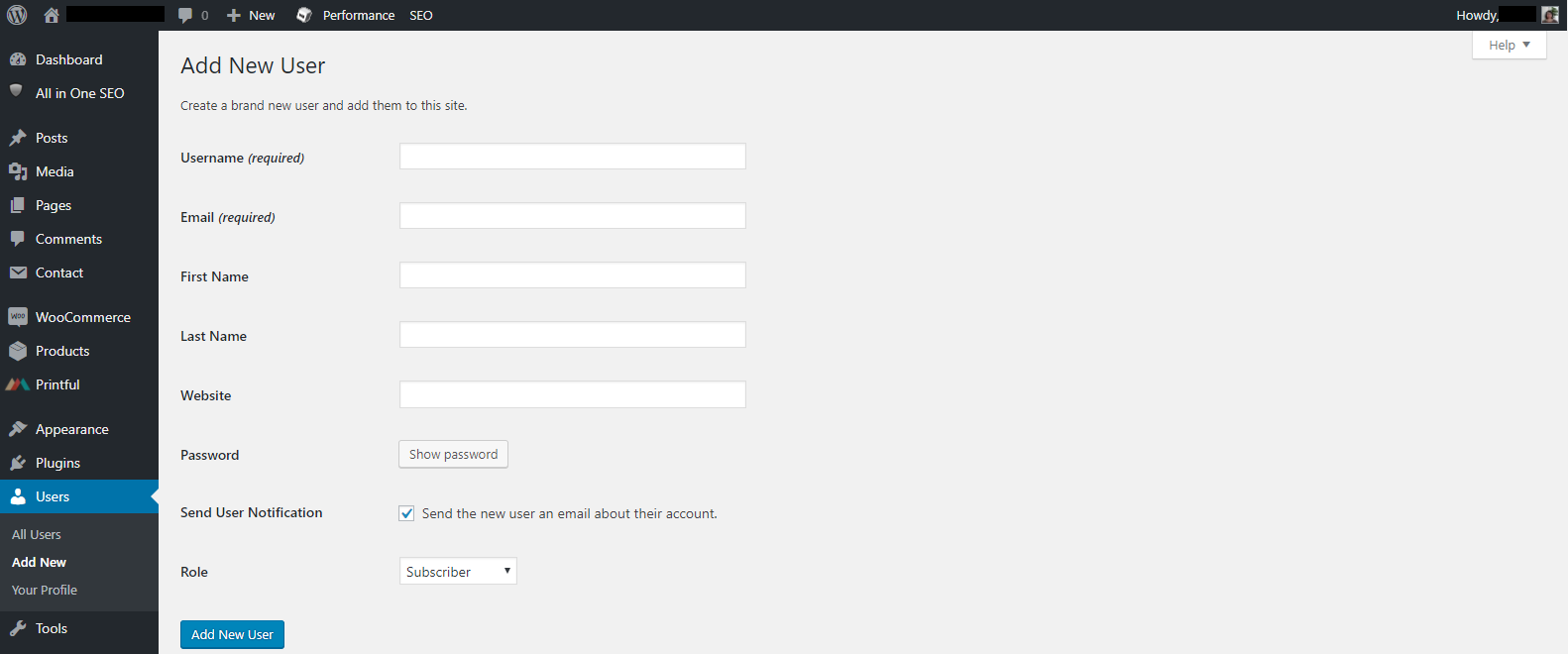
Now that you know more about user roles, you can effectively assign them to your team or collaborators. It’s a good idea to limit the number of Admins and assign permissions as needed. If you want to customize the permissions, you could use a plugin to do so.
Additional info
For more details about roles, you can go to the WordPress Codex on User Roles.
https://codex.wordpress.org/Roles_and_Capabilities
Here is an article about user role plugins:
